Monitoring Tools to Control Server Sprawl
According to the Microsoft SQL Server team on TechNet , SQL Server is world’s most widely deployed database. In its October 2013 magic quadrant, Gartner identified Microsoft as a leader, second only to Oracle.
Magic Quadrant for Operational Database Management Systems
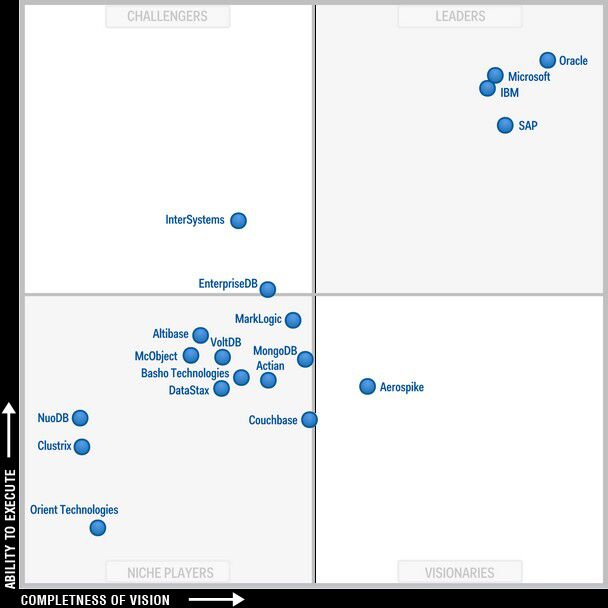 Source: Gartner (October 2013) – http://gtnr.it/IKDu9G
Source: Gartner (October 2013) – http://gtnr.it/IKDu9G
SQL Server’s success is attributed to multiple factors:
- It is simple to install and easy to maintain.
- Several third party applications and development tools support SQL server.
- It has a wide array of functionalities and with the scalability enhancements in its latest releases, it represents a good option for enterprises.
- Microsoft also provides lower cost, service-provider friendly licensing that makes deployment of SQL easy.
SQL Server Proliferation Results in Sprawl
The very success of SQL server has contributed to a high degree of proliferation, leading to SQL server sprawl. Almost all applications today use a database server for data storage. Because of its licensing and ease of use, many packaged applications and in-house applications use SQL server as the backend. To minimize conflict between applications, many a times, a separate SQL server or SQL instance is used for each application.
Since it is simple to deploy, application owners themselves often deploy and use SQL server, instead of depending on a database administration team. Over a period, this uncoordinated deployment has resulted in a proliferation of SQL server instances, leading to SQL sprawl.
Yet another artifact of this evolution is that an enterprise often has multiple versions of SQL server running in parallel. A recent survey conducted by Paul S. Randal shows that enterprises are still running several older versions of SQL server. In fact, as the table below reveals 45% of enterprises still have SQL Server 2000 deployed!
What’s the oldest version of SQL Server that you have in production?
Source: SQLSkills.com – http://bit.ly/1dnRpvj
What makes the problem worse is the fact that often, when an application is decommissioned, the database server it uses has to be manually decommissioned. This also results in SQL server instances being left running but not used.
From a resource usage perspective, for optimal performance, SQL server has been designed to use up all of the memory available on the servers (or VMs) that it is hosted on. If there are unused instances of SQL server running, these will unnecessarily take up a lot of the memory resources. In environments where SQL server is deployed on virtual machines, the bloated memory usage of unused SQL instances could even impact the performance of applications hosted on other virtual machines.
The Need for Unified Monitoring of Microsoft SQL Server
To manage SQL server in an enterprise, the IT team needs to be able to:
- Automatically discover all the systems where SQL server is running;
- Be able to monitor all the SQL instances, to determine ones that are least used or rarely used;
- For the ones that are in use, determine if the resources allocated for each instance are optimal or not.
- Measure the performance of each SQL server instance to determine the availability and responsiveness of each instance.
- Have a consistent way to monitor different versions of SQL server, so administrators do not have to learn different tools for each version.
eG Enterprise provides IT administrators a single, integrated monitoring solution using which they can monitor, diagnose and report on the performance of SQL Server across all of the commonly deployed versions and in a consistent manner. SQL versions 7.0, 2000, 2005, 2008, and 2012 are supported. Monitoring of named and port-based SQL instances is supported and SQL clusters can also be monitored from the same console. IT administrators also have the option of monitoring SQL Server in an agent based or agentless manner. For more information on the eG SQL monitor, see https://www.eginnovations.com/sql-server-monitoring
eG Enterprise is an Observability solution for Modern IT. Monitor digital workspaces,
web applications, SaaS services, cloud and containers from a single pane of glass.

