Introduction
The Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) is a data center computing solution composed of computing hardware, virtualization software, switching fabric, and management software. The idea behind the system is to reduce total cost of ownership and improve scalability by integrating the different components into a cohesive platform that can be managed as a single unit. Just-In-Time deployment of resources and 1:N redundancy are also possible with a system of this type.
Figure 1 depicts the architecture of Cisco UCS.
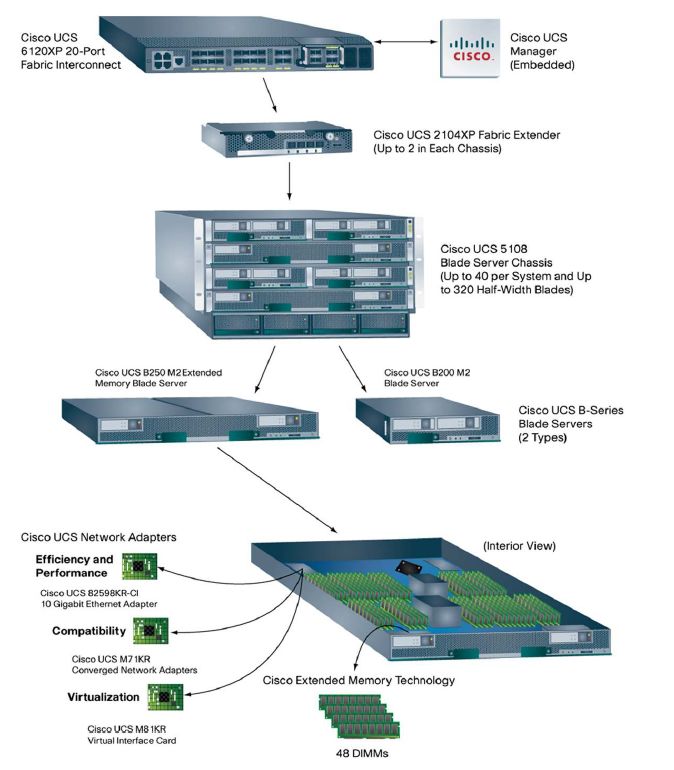
Figure 1 : The architecture of the Cisco UCS
The computing component of the UCS is available in two versions; the B-Series (a modular package consisting of a powered chassis and full or half slot blade servers), and the C-series rackmount servers (that can be used with or without UCS, or mixed with blade UCS systems). Both form factors utilize the same standard components seen throughout the industry, including Intel Nehalem processors and DIMM memory. The servers are distinctive for supporting Converged Network Adapters ( CNAs), Port Virtualization, and in some models the Catalina chipset (ASICs that expand the number of memory sockets than can be connected to a single memory bus).
Besides the blade servers and chassis, the other core components of the Cisco UCS are as follows:
- UCS manager: Cisco UCS Manager implements policy-based management of the server and network resources. Network, storage, and server administrators all create service profiles, allowing the manager to configure the servers, adapters, and fabric extenders and appropriate isolation, quality of service (QoS), and uplink connectivity. It also provides APIs for integration with existing data center systems management tools. An XML interface allows the system to be monitored or configured by upper-level systems management tools.
- UCS fabric interconnect: Networking and management for attached blades and chassis with 10 GigE and FCoE. All attached blades are part of a single management domain. Deployed in redundant pairs, the 20-port and the 40-port offer centralized management with Cisco UCS Manager software and virtual machine optimized services with the support for VN-Link.
- Cisco Fabric Manager: manages storage networking across all Cisco SAN and unified fabrics with control of FC and FCoE. Offers unified discovery of all Cisco Data Center 3.0 devices aa well as task automation and reporting. Enables IT to optimize for the quality-of-service (QoS) levels, performance monitoring, federated reporting, troubleshooting tools, discovery and configuration automation.
- Fabric extenders: connect the fabric to the blade server enclosure, with 10 Gigabit Ethernet connections and simplifying diagnostics, cabling, and management. The fabric extender is similar to a distributed line card and also manages the chassis environment (the power supply, fans and blades) so separate chassis management modules are not required. Each UCS chassis can support up to two fabric extenders for redundancy.
The health of the Cisco UCS platform hence largely relies on how the blade chassis, the blade servers, the fabric interconnects and extenders are functioning. This implies that issues in the availablity / operability of one/more of these components, or the unexpected power/thermal/voltage failures they may encounter can degrade the overall performance of the Cisco UCS. In order to avoid this, the health and operational efficiency of the integral components of the platform should be continuously monitored, and issues proactively reported. This can be easily achieved using eG Enterprise.



