How Does eG Enterprise Monitor Cloud Desktops?
eG Enterprise monitors cloud desktops in an agentless manner.
Pre-Requisites for monitoring Cloud Desktops
-
For internal monitoring of the individual Windows desktops on the cloud, a light-weight eG VM Agent has to be installed on each of the desktops.
Typically, when monitoring the Windows desktops on hypervisors such as VMware vSphere, Citrix Hypervisor, etc., the eG remote agent installed on a remote Windows/Linux host in the environment communicates with the hypervisor to automatically discover the IP address and host name of every virtual desktop on that hypervisor. With this information, the remote agent then polls the eG VM Agent on each Windows desktop for inside view metrics. The eG VM Agent is bundled with the commands and executables necessary for capturing inside view metrics. Every time the remote agent requests the eG VM agent for metrics, the eG VM Agent automatically runs the built-in commands/exes for metrics collection. Once the metrics are collected, the remote agent then pulls these metrics from the eG VM Agent on each desktop and reports them to the eG manager.
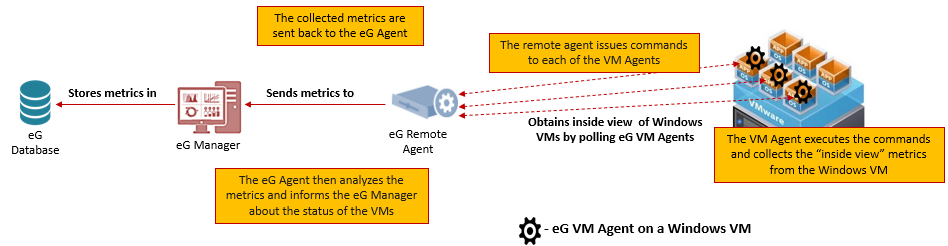
Figure 2 : The eG Remote Agent - eG VM Agent communication when monitoring desktops on a hypervisor
In the case of a Cloud desktop too, an eG remote agent on a remote Windows/Linux host is used for monitoring. However, unlike the hypervisor scenario, here, the remote agent does not initiate any communication with the eG VM Agent on the individual Windows desktops on the cloud. This is because, this remote agent has no knowledge of the hypervisor on which the cloud desktops are operating. Therefore, it can neither discover the IP address/host name of the cloud desktops, nor can it communicate with them to collect the 'inside view' metrics.
This is why, the eG VM Agent on a Windows cloud desktop has been specifically engineered to initiate all communication. The eG VM Agent on a cloud desktop first communicates with the eG manager to know which remote agent has been assigned to that Windows desktop. Then, the eG VM Agent pushes the cached 'inside view' metrics to that remote agent via TCP. To enable this communication, a TCP port has to be opened on the eG remote agent. If the remote agent is behind a firewall, then make sure that the firewall is configured to allow one-way communication from the eG VM agent to the remote agent. Upon receipt of the 'inside view' metrics, the remote agent sends the metrics to the eG manager.
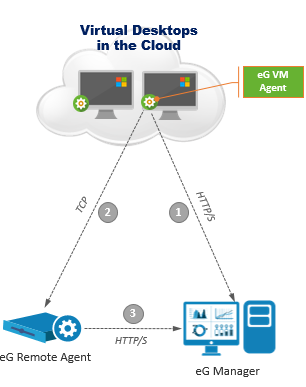
Figure 3 : The eG VM Agent - eG Remote Agent communication when monitoring desktops on the cloud
-
When monitoring Cloud Desktops, the remote agent needs to be in the same subnet as that of the eG VM Agent or accessible on the local network of the eG VM Agent.
-
Ensure that the eG VM Agent communicates with the IP address of the remote agent directly and that the communication is not via a NAT or port forward.



