Introduction
everRun VM delivers reliable protection for critical virtual workloads by providing redundant virtual machines and synchronized mirroring of the entire system – network, applications and data. It protects at the individual VM level, but runs below the VM, just above the hypervisor. This level of integration allows everRun to build redundancy that is completely transparent to the operating environment to seamlessly manage failures while the application continues to execute. This is called ComputeThru technology. Where Citrix XenServer is used to provision multiple Windows virtual machines on a single physical server, you can use everRun to protect the Windows VMs and their applications from failures.
To understand how everRun VM works, consider a simple case. Assume that two identical Intel or AMD-based physical servers are available in your environment. These servers are configured with Ethernet adapters for application use and either local (direct-attached) or shared storage. Redundant Ethernet paths, known as Availability Links, provide a private communications path used by everRun to maintain synchronization of storage and application operations for the virtual machines that everRun protects. Each server should run the XenServer Enterprise Edition virtualization software as the host environment. The everRun technology is loaded as a virtual appliance (the everRun Availability Manager). The Availability Manager runs within the XenServer environment as a purpose-built appliance that provides availability for other virtual machines on the host. The Availability Manager establishes a tightly-coupled relationship to the virtual machines it protects. It resides in the data path between the virtual machine and the control domain, which handles I/O for the virtual machines. To protect a virtual machine, the administrator uses the everRun Availability Center to indicate which virtual machine to protect with everRun and then selects the desired protection level and which host to use for protection. Once this is done, everRun transparently combines and manages the resources of two virtual machines running on different servers in a XenServer resource pool to create a single protected virtual machine environment. The protected virtual machine (PVM) appears and is managed just like a standard Windows server. Disk data is mirrored synchronously to redundant storage and network and server operations are protected from failure. The administrator can load and configure applications in the protected virtual machine, as though it was being loaded onto a physical server.
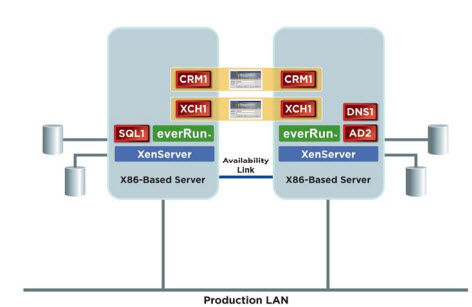
Figure 1 : How everRun VM works
Since the PVM provides users with a fail-proof virtual machine environment, many enterprises host their mission-critical applications on VMs that are protected by everRun. Problems with the PVM therefore – eg., errors experienced by the PVM, disk and network failures suffered by the PVM – will lift the veil of protection that everRun offers, and expose the protected VMs, applications, network, and data to problems. To avoid this, you need to continuously track the status of the PVM, its disk and network resources, and the XenServer hosts it protects, so that potential errors in the functioning of the PVM are proactively detected and removed, and the protected VMs and applications operate without any interruptions. This is where eG Enterprise helps administrator.



