Introduction
Virtual Server 2005 R2 is a cost-effective server virtualization technology engineered for the Windows Server System™ platform. As a key part of any server consolidation strategy, Virtual Server increases hardware utilization and enables organizations to rapidly configure and deploy new servers. It improves operational efficiency in consolidating infrastructure, applications, and branch office server workloads, consolidating and re-hosting legacy applications, automating and consolidating software test and development environments, and reducing disaster impact.
Virtual Server 2005 R2 is a multithreaded application that runs as a system service, with each virtual machine running in its own thread of execution; I/O (input/output) occurs in child threads. Virtual Server 2005 R2 derives two core functions from the host operating system: 1) the underlying host operating system kernel schedules CPU resources, and 2) device drivers of the host operating system provide access to system devices. The Virtual Server 2005 R2 Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) provides the software infrastructure to create virtual machines, manage instances, and interact with guest operating systems. Figure 1 illustrates the Virtual Server 2005 R2 architecture.
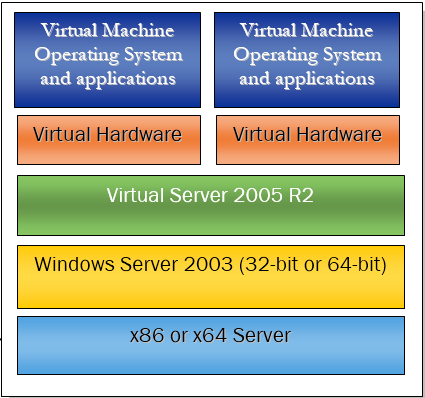
Figure 1 : Virtual Server architecture
As the individual VMs on a Microsoft Virtual server share the CPU resources and device drivers of the host, resource contention at the host can degrade the performance of the VMs and the applications executing on them. At the same time, resource-intensive processes/applications executing on one/more guests can also erode the resources allocated to the guests and consequently affect application health. If one/more of these virtualized applications are participating in the delivery of a critical end-user service, then slowdowns experienced by the applications can adversely impact the service quality. Service operators should therefore carefully observe the resource usage of guests both from within and outside the guests, and accordingly fine-tune resource allocations, so as to ensure the optimal performance of the virtual infrastructure and the business-critical service riding on it. This is where eG Enterprise helps administrators.
