Introduction
Oracle PeopleSoft Internet Architecture (PIA), leverages a number of internet technologies and concepts to deliver simple, ubiquitous access to PeopleSoft applications and enable the open flow of information between systems. Using PeopleSoft Internet Architecture as the foundation, customers will be able to provide a wide range of end users with access to PeopleSoft applications over the web, as well as more easily integrate their PeopleSoft applications with existing internal systems and external trading partner systems.
The PeopleSoft Internet Architecture is comprised of these main server types:
- RDBMS
- Tuxedo Application Server(s)
- Web server(s)
The servers facilitate connections and process requests from:
- PeopleTools Development Environment: A Windows workstation running a development tool, such as PeopleSoft Application Designer.
- Browser: A supported browser type and version displaying a PeopleSoft application or administrative interface.
- Remote system: A PeopleSoft or third-party system integrated through PeopleSoft Integration Broker’s service oriented architecture (SOA).
The following diagram illustrates the relationship between the elements of the PeopleSoft Internet Architecture.
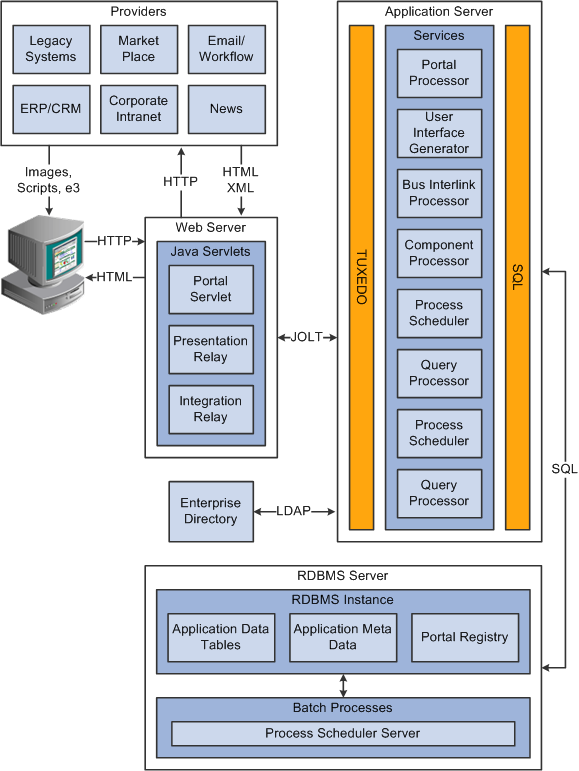
Figure 1 : How the PeopleSoft Internet Architecture operates
As is evident from the image, application requests are received by the web server using three PeopleSoft servlets – namely, the Presentation Relay Servlet, the Integration Relay Servlet, and the Portal Servlet. When a PeopleSoft application sends a request, it sends a service name and a set of parameters. Any request so received is then forwarded by the web server to the Tuxedo application server. The application server then queues the transaction request to a specific server process that is designed to handle certain services.
An application server consists of numerous PeopleSoft server processes, grouped in domains. When you boot an application server domain, it starts the set of server processes associated with that domain. Each server process establishes a persistent connection to a PeopleSoft database, and this connection acts as a generic SQL pipeline that the server process uses to send and receive data. Listeners, handlers, and queues in a domain receive requests, route requests, store requests, monitor requests, and return request responses.
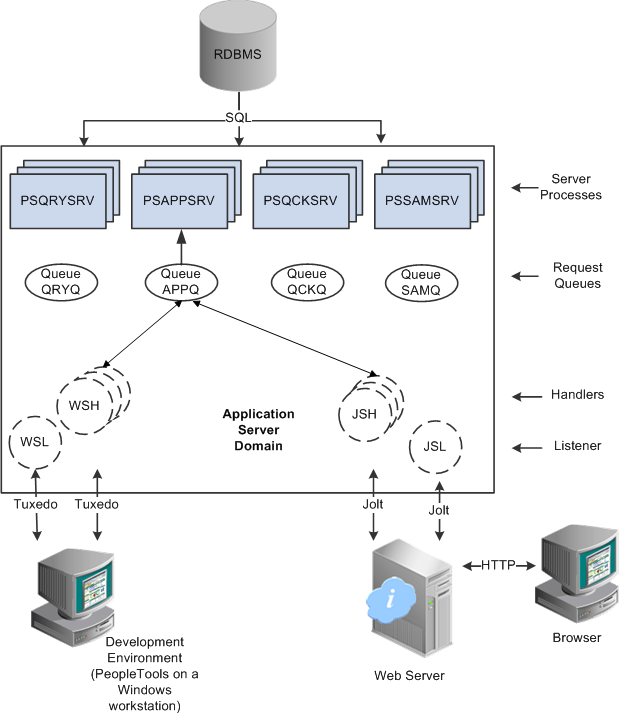
Figure 2 : How an application domain processes requests
The proper functioning of all these crucial elements – be it the server processes, services, listeners, handlers, and queues in a domain – is essential to ensure that the domain effectively handles application requests, and that users have an above-par experience with PeopleSoft applications at all times.
