Configuring the eG Manager's JMX with Authentication
This involves three broad steps:
-
Configuring a 'special monitor user' with read-write access to the eG manager's JMX;
-
Enabling Authentication support for JMX and allowing JMX access to the 'special monitor user'
-
Protecting the Password file (which will be created at step 1 above) from unauthorized access
Each of the above-mentioned steps are discussed elaborately in the sections below:
Configuring a Special Monitor User with Read-Write Access to JMX
If the eG agent needs to use JMX for monitoring the eG manager, and this JMX requires authentication only (and not security), then every test to be executed by such an eG agent should be configured with the credentials of a valid user to JMX, with read-write rights. The steps for creating such a user are detailed below:
- Login to the system hosting the eG manager. If the eG manager being monitored is on a Windows host, then login as a local/domain administrator to the host.
-
Go to the <java_home>\jre\lib\management folder used by the eG manager to view the following files:
- management.properties
- jmxremote.access
- jmxremote.password.template
- snmp.acl.template
-
Copy the jmxremote.password.template file to a different location, rename it as jmxremote.password, and copy it back to the <java_home>\jre\lib\management folder.
-
Open the jmxremote.password file and scroll down to the end of the file. By default, you will find the commented entries indicated by Figure 1 below:

Figure 1 : Scrolling down the jmxremote.password file to view 2 commented entries
- The two entries indicated by Figure 1 are sample username password pairs with access to JMX. For instance, in the first sample entry of Figure 1 monitorRole is the username and QED is the password corresponding to monitorRole. Likewise, in the second line, the controlRole user takes the password R&D.
-
If you want to use one of these pre-defined username password pairs during test configuration, then simply uncomment the corresponding entry by removing the # symbol preceding that entry. However, prior to that, you need to determine what privileges have been granted to both these users. For that, open the jmxremote.access file in the editor.

- Scrolling down the file (as indicated by Figure 2) will reveal 2 lines, each corresponding to the sample username available in the jmxremote.password file. Each line denotes the access rights of the corresponding user. As is evident from Figure 2, the user monitorRole has only readonly rights, while user controlRole has readwrite rights. Since the eG agent requires readwrite rights to be able to pull out key JVM-related statistics using JMX, we will have to configure the test with the credentials of the user controlRole.
-
For that, first, edit the jmxremote.password file and uncomment the controlRole <password> line as depicted by Figure 3.

- Then, save the file.
- You can now proceed to configure the tests with the user name controlRole and password R&D.
- Alternatively, instead of going with these default credentials, you can create a new username password pair in the jmxremote.password file, assign readwrite rights to this user in the jmxremote.access file, and then configure the eG tests with the credentials of this new user. For instance, let us create a user john with password john and assign readwrite rights to john.
-
For this purpose, first, edit the jmxremote.password file, and append the following line (see Figure 4) to it:
john john

- Save the jmxremote.password file.
-
Then, edit the jmxremote.access file, and append the following line (see Figure 5) to it:
john readwrite

Figure 5 : Assigning rights to the new user in the jmxremote.access file
- Then, save the jmxremote.access file.
- Finally, proceed to configure the tests with the user name and password, john and john, respectively.
Note:
If you are trying to enable JMX on a Linux host, you might encounter issues with the way hostnames are resolved.
To solve it you might have to set the -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=<hostname or localhost or ip> property in the startup script of theeG manager.
If you are in local, simply try with -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=localhost or -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=127.0.0.1.
Enabling Authentication for the eG Manager's JMX
To enable 'Authentication' for the eG manager's JMX, do the following:
-
Login to the system hosting the eG manager.
-
Edit the management.properties file in the <JAVA_HOME>\jre\lib\managementfolder (on Windows; on Unix, this will be the /opt/jre/lib/management folder).
-
You will find the following code block in the file, by default:
com.sun.management.jmxremote.port=13600
com.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
com.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
-
To enable Authentication, change the code block as indicated by the line in Bold below:
com.sun.management.jmxremote.port=13600
com.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=true
com.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
-
Then, append the following lines to the code block, so that the 'special monitor user' (configured using the procedure detailed in Section 1.1 above) is allowed JMX access.
com.sun.management.jmxremote.access.file=<Full_path_to_the_jmxremote.access_file>
com.sun.management.jmxremote.password.file=<Full_path_to_the_jmxremote.password_file>
For instance, if the jmxremote.access and jmxremote.password files are in C:\Java\jre\lib\management folder, then the above code block will be:
com.sun.management.jmxremote.access.file=C:\Java\jre\lib\management\
jmxremote.access
com.sun.management.jmxremote.password.file=C:\Java\jre\lib\management\
jmxremote.passwprd
-
Finally, save the management.properties file.
Protecting the Password file from Unauthorized Access
To enable the eG agent to communicate securely with JMX, you need to make the jmxremote.password file secure by granting a single user “full access” to that file. For monitoring an eG manager on Windows in particular, only the Owner of the jmxremote.password file should have full control of that file. To grant this privilege to the Owner of the file, follow the steps below:
- Login to the Windows server hosting the eG manager as a local/domain administrator.
- Browse to the location of the jmxremote.password file using Windows Explorer.
-
Next, right-click on the jmxremote.password file and select the Properties option (see Figure 6).

-
From Figure 7 that appears next, select the Security tab.

-
Next, click on the Advanced button in the Security tab of Figure 7. Figure 8 will then appear displaying the Owner of the jmxremote.password file.
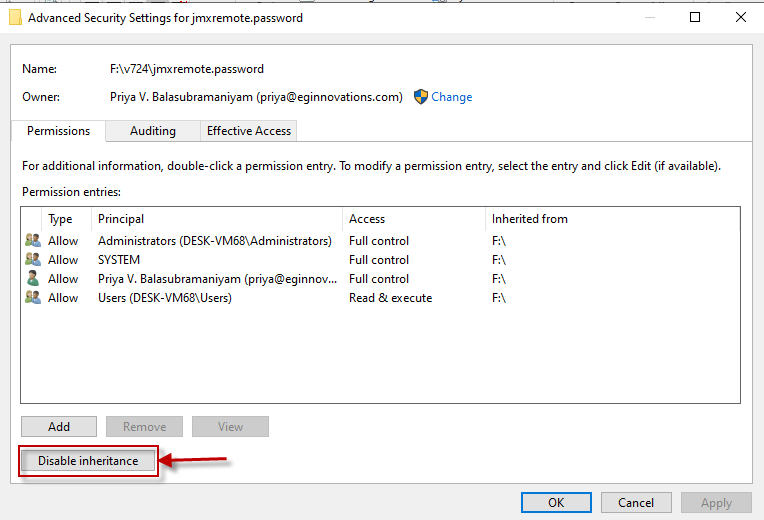
Figure 8 : Viewing the Owner of the Password file and setting access permissions
-
Then, proceed to set the access permissions for the file using the Permissions tab that opens by default (see Figure 8). If the jmxremote.password file has inherited its permissions from a parent directory that allows users or groups other than the Owner to access the file, then click on the Disable inheritance button in Figure 9. Figure 9 will then appear. Here, you will be prompted to confirm whether the inherited permissions should be converted and applied as explicit permissions, or removed. Click on the Convert inherited permissions into explicit permissions on this object option in Figure 9.
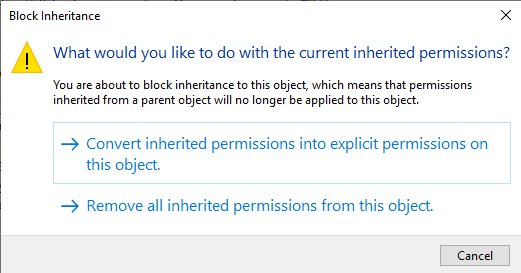
Figure 9 : Converting inherited permissions into explicit permissions
-
When Figure 10 appears, remove all permission entries that allow users (or groups) other than the Owner to access the jmxremote.password file. For this, click the user or group and press the Remove button in Figure 10. At the end of this exercise, only a single permission entry granting Full Control to the owner should remain in Figure 10.

- Finally, click the Apply and ok buttons to register the changes. The password file is now secure, and can only be accessed by the file owner.



