Introduction
Microsoft Application Virtualization, also known as App-V; is an application virtualization and application streaming solution. Microsoft Application Virtualization enables the administrator to deploy, update, and support applications as services in real time, on an as-needed basis. When App-V is used, individual applications are transformed from locally installed products into centrally managed services. Applications become available everywhere they need to be—no computer pre-configuration or changes to operating system settings are required. Microsoft Application Virtualization consists of the following components:
- Microsoft App-V Management Server, which provides a centralized location to manage the App-V infrastructure for delivering virtual applications to both the App-V Desktop Client and the Remote Desktop Services (formerly Terminal Services) Client. The App-V Management Server uses Microsoft SQL Server for its data store, where one or more App-V Management servers can share a single SQL Server data store. The App-V Management Server authenticates requests and provides the security, metering, monitoring, and data gathering required by the administrator. The server uses Active Directory and supporting tools to manage users and applications. The App-V Management Server has a Silverlight-based management site, which enables administrators to configure the App-V infrastructure from any computer. By using this site, administrators can add and remove applications, manipulate shortcuts, assign access permissions to users and groups, and create connection groups. The App-V Management Server is the communication conduit between the App-V Web Management Console and the SQL Server data store. These components can all be installed on a single server computer, or on one or more separate computers depending on the required system architecture.
- Microsoft App-V Publishing Server, provides App-V clients with entitled applications for the specific user and hosts the virtual application package for streaming. The Publishing Server can either be installed on the same machine as the Management Server or can be installed on separate machines. In live environments, separate installation provides greater scalability of the infrastructure.
- Microsoft App-V Application Virtualization for Desktops, also called App-V client, retrieves virtual applications, publishes the applications on the client, and automatically sets up and manages virtual environments at runtime on Windows endpoints. The App‑V Client stores user-specific virtual application settings, such as registry and file changes, in each user’s profile.
- Microsoft App-V Remote Desktop Services (RDS) Client, enables Remote Desktop Session Host servers to utilize the capabilities of the App-V Desktop Client for shared desktop sessions.
- Microsoft App-V Virtualization Sequencer is a wizard-based tool that administrators use to transform traditional applications into virtual applications. The Sequencer produces the application “package”, which consists of several files. These files include a sequenced application (APPV) file, a Windows Installer file (MSI) that can be deployed to clients configured for standalone operation, and several XML files including Report.XML, PackageName_DeploymentConfig.XML, and PackageName_UserConfig.XML. The UserConfig and DeploymentConfig XML files are used to configure custom changes to the default behavior of the package.
- App-V Management Console, the management tool to set up, administer and manage App-V servers. It can be used to define policies that govern the usage of the applications. It can also be used to create, manage, update and replicate virtualized application packages.
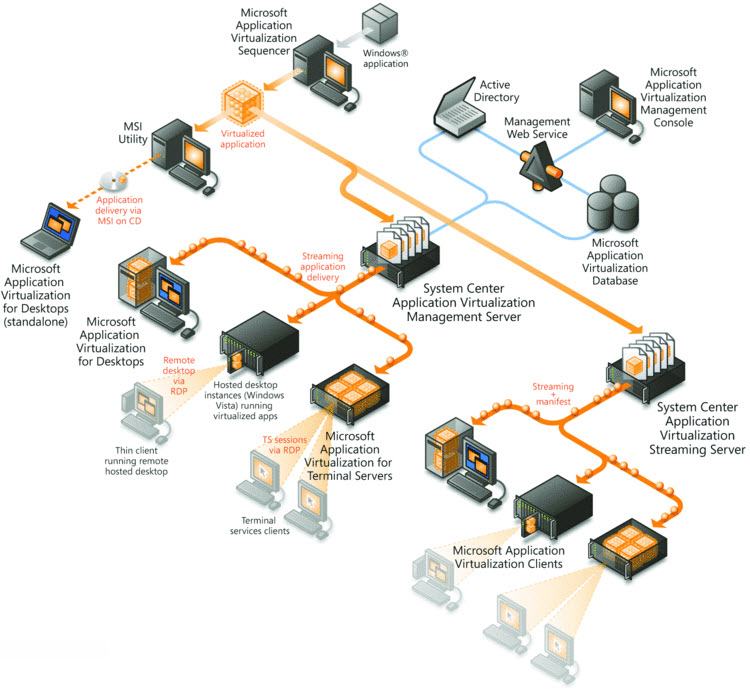
Figure 1 : The components of an App-V architecture
Quick and easy access to published applications enables administrators a 'good user experience' with the APP-V server. On the contrary, application slow-downs can be the key spoilers of a user's experience with the APP-V server. More frustrating to administrators is the fact that many times, the cause of such anomalies cannot be pinpointed, making recovery difficult. While standard monitoring solutions are available, most do not provide the critical in-depth analysis that administrators need, with many failing to provide comprehensive data into the network, storage, virtualization and application levels. Administrators thus far have been pressured to discover the reasons behind network performance failures, unable to pinpoint the problem to the network, profile server, Web access, virtualization platform or other components.
To meet the high standards of network administrators, eG App-V Monitoring provides total performance visibility for App-V installations of all types. As part of the eG Enterprise, eG App-V Monitoring is a comprehensive management solution which provides complete visibility and monitoring for all layers and tiers of the organization’s APP-V infrastructure, including the APP-V Management server, and the App-V Client.
Towards this end, eG Enterprise offers two



